Please double-check your email address when placing an order. A correct email ensures you receive shipping updates and don’t miss your package.
If you don’t see our emails, check your Spam folder.
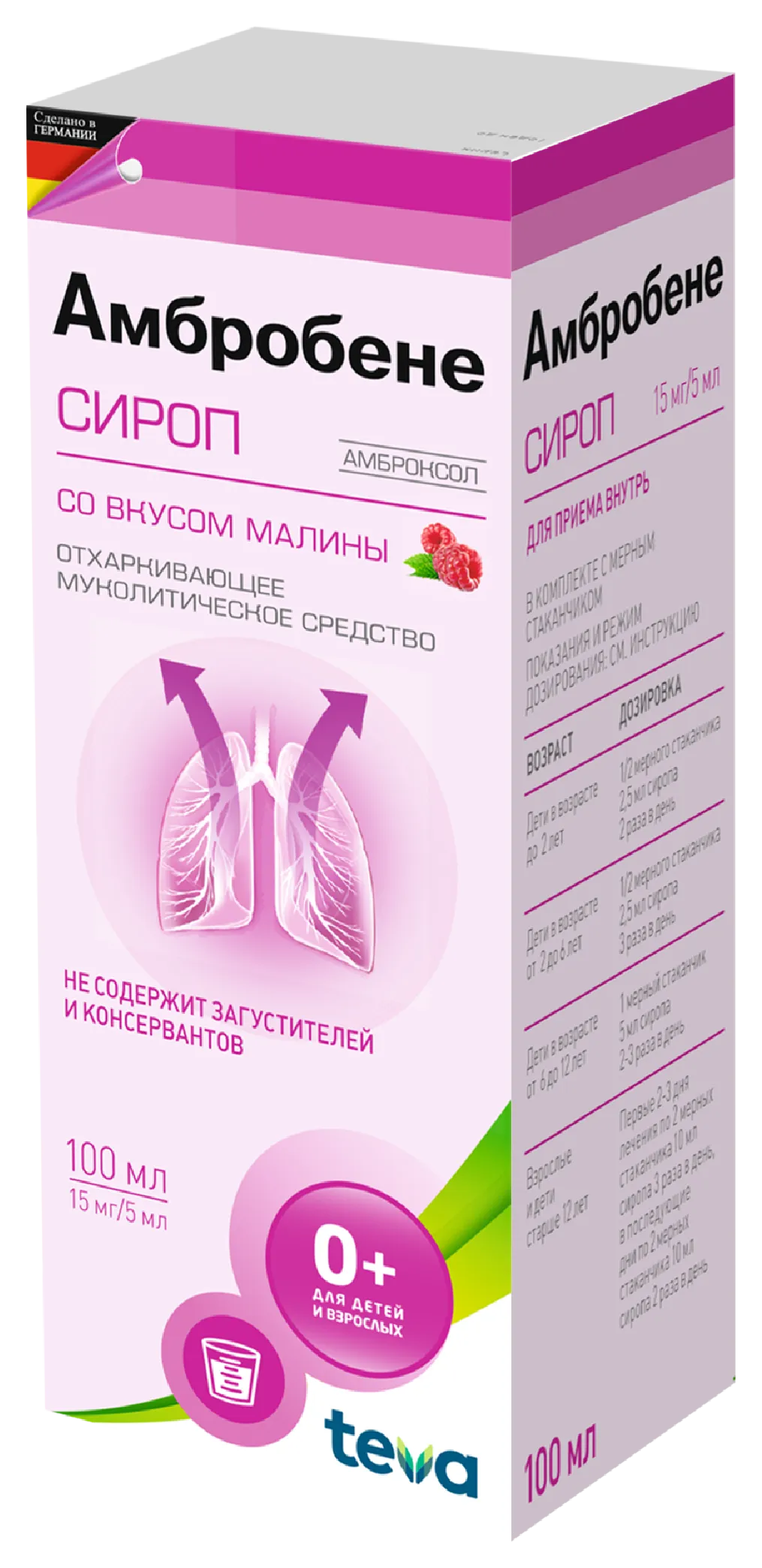
Ambrobene syrup 100 ml
⛟ Same day shipping
❤ Free US shipping on Orders $69+
☎ Can’t find it? Ask us via WhatsApp, phone or chat
💰Bonus program
We have run out of stock for this item.
Ambrobene syrup 100 ml
If this product is temporarily out of stock, consider: Herbion Syrup with Primula Veris Extract 150 ml
Ambrobene is a mucolytic syrup containing ambroxol at a concentration of 15 mg/5 ml, intended for the treatment of respiratory diseases with difficulty in sputum discharge. The primary action of the preparation is aimed at thinning the sputum and improving its clearance, which facilitates the breathing process. It is used for bronchitis, pneumonia, and other respiratory diseases in children and adults. The product starts acting 30 minutes after intake and maintains its effect for up to 6-12 hours.
*We apologize for any inconvenience in case of the product being out of stock.
Please feel free to use this form to contact us, and we will notify you as soon as the item is available again.
Here's something that might pique your interest:
The Correlation between Gut Health and Overall Well-being
In our blog, you can discover a wealth of fascinating and valuable information.
Thank you for choosing USA Apteka, your Russian pharmacy and trusted source for popular, favorite OTC products from Russia, Ukraine, and other CIS countries.
Important
Use
Warnings
Please Chat with us or send us a message on WhatsApp